Heads up not only for Personal trainers
Principle one
The joint configuration patterns are:
- Children of preschool age as of 3 months of their age, before their motion system is “handicapped” by the sedentary way of life, starting with school. In the repertoire of children moving in the healthy way there is included even the motion of our ancestors, for example scrambling and partially climbing on the trees.
- Experienced athletes in the strength disciplines, partially even in martial arts and oriental health techniques – tai ji, qi gong.
- Experienced workers, for example those manipulating with freightage and overcoming large resistance.
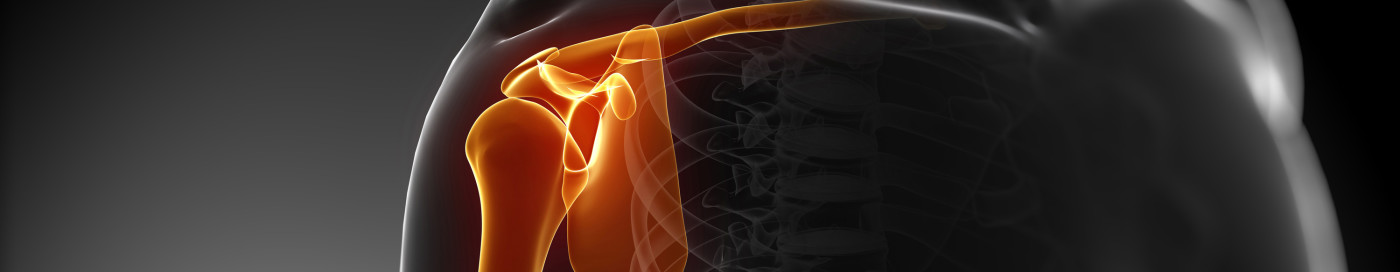
- The joint configuration in manual medicine (for example centralization of shoulder), in therapeutic or health TV.
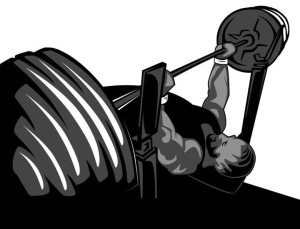
If we compare the positioning of shoulder joint by a child during scrambling and an athlete providing bench press, we can see similar configuration, which is manifestation of functional centralization. The same applies during squat of child and athlete.
Priciple two
Exercising with the joints in the centralized positions function as motion treatment but also prevention of muscle misbalances.
Alignment of joints into the centralization, resistance against the stabilization (often against the vericalisation or locomotion) and cooperation of the trainee (his goals, visualizations, and focus) – all that helps the joint stabilization including corresponding CNS.
During the joint alignment into the function centralization and during adequate resistance against natural human activities, which are for example verticalisation, locomotion, manipulation with weights and transportation of the body in space, where to belongs exercising in hanging position and its modifications the brain is receiving physiological information. Joint configurations are deciding what programs the brain will choose and which commands for the stabilization of joint it will respond with: during alignment of joints into centralization rich flow of information is coming up from the periphery into the center.
This is called afferent set in the technical terms and it basically means the flow of information coming into the brain at certain period of time. We are interested in maximal summation of physiological information, that is why we intentionally align utmost joints into centralization.
Indispensable are the projections of the trainee (for example that on his/her head there is a crock) the projection of what he needs to do, his focus and checking of feelings, which are then reported to the trainer. If we train by ourselves, we have to sub the job of the trainer and correct ourselves according to predefined subjective and objective criteria.
Principle three
For practice of centralization of joints it is suitable usage of adequate resistance: first really small, following on the edge of its manageability.
By this extreme situation we will wake up the brain to activate the prime (human, genetically evolved) programs, which we have covered by non adequate, convenient and hypokinetic way of life and programs which are harmful for us and are not even physiological. This muscle exercising is shifting the coordination strength functional reserve and it is becoming not only stimuli for gaining of muscle strength, but also a teacher of muscle coordination during the joint stabilization.
Exercising on the edge of its manageability is embodies great effectivity of motor learning.
In this content the strength training is medical and preventative aid not only for the motion system, but for a man as a whole. We focus on the stabilization of spine the most and that means not only in the anterior (front) / posterior (back) plane and right/left (sagittal) but also in the directions crossing, diagonal and rotational.
Principle four
For the stimulation of the diagonal stabilization chains we choose unilateral exercises.
During unilateral training the diagonal and torsional tension rises, this stabilize the spine and other joints. That is why if we can (if we manage), we exercise one arm at a time. Typically human loops are coming up from our crossed locomotion and from the need of joint stabilization in every direction. As said before, in the evolution of an individual the first stabilization coming up is the sagittal stabilization, followed by the stabilization in the diagonal directions, first during rotating (after 4th month of age) in the way of homolateral or ipsilateral, when the support depends on limbs of side of the body. Later (after 7th month of age) the scrambling happens and this leads to the crossed locomotion and the corresponding stabilization. The support is on the opposite limbs, for example on upper left arm and lower right leg and the rest opposite limbs are phasic. While walking we don’t use arms for support as during scrambling. All the support relies on legs and arms (using inertial energy) are inducing tension in the body similarly to hand-hold. For example, during finishing the step on your right foot the left arm is suddenly changing (moving until that time forward) the direction of the motion. At the beginning of this changed motion backwards the muscles providing adduction have to suddenly pull. These are the same muscles, which are activated during the scrambling thus adductors (in this case left arm), for example chest muscles and latissimus dorsi. The most important muscles for stabilization are the muscles located deep: rotators of spine, deep abdominal muscles and diaphragm with pelvic floor, …
The stabilization muscles are in close attention to us during unilateral exercising (we should not forget the fixators of the shoulder blades). Of course we cannot use only unilateral exercises, because we have to stabilize the body also in the sagittal, frontal, … plane.
Principle five
Preference of the frontal plane stabilization
Frontal plane stabilization is the primary in the evolution and that is why we should not forget it during the training. It is action to the surrounding in the frontal plane with predominance of stabilization by the deep muscles located either in the front or the back side of the body.  The typical representative of the stabilization in the front (ventral) you can find later on in my posts as well as dorsal ones. Even though we speak about superiority of the abdominal or back muscles, the stabilization is secured by cooperation of the (deep) motor units on both side of the body.
The typical representative of the stabilization in the front (ventral) you can find later on in my posts as well as dorsal ones. Even though we speak about superiority of the abdominal or back muscles, the stabilization is secured by cooperation of the (deep) motor units on both side of the body.
Principle six
From the center to the periphery and from the periphery to the center
I have mentioned this principle earlier – from the center to the periphery. We understand it above all in the sense of activation of muscles (to be exact their parts) from the deep (stabilization) to the surface once. From the center to the periphery there is also going on response from the training in the sense that first the processes in the CNS are happening and only after the changes in muscles and tissues or liquids in the body. To change the way of control (change in the center) is much easier for the organisms than to change the periphery. We can compare it to the change of software in the PC which is much easier and faster than upgrading the hardware of the PC. In human the change of the program can happen almost immediately under the right conditions. For example, he or she can learn during several minutes to stabilize shoulder-blade. Change of the metabolism of muscles or trophic takes a bit longer.
For training of the rotators – spinotransversal system responsible for stabilization of spine it is suitable to work out using unilateral exercises (with cable, dumbbells, … ) but most of all using arm support. This way we will ensure exercising of the deep diagonal stabilization muscles, even though there is no active rotation of trunk or at least it is not apparent.
From the periphery to the center or from the point of support to the center we stabilize our body together with strengthening from the center. The information about stabilization of the body are coming from the place of support to the moving parts thanks to the surface contact. That does not mean this situation is happening only during walking (from soles through ankles, knees, hips and trunk towards arms and head) but also for example during sitting by the cable pulley. Even in this case the information is transferred not only from pelvis towards trunk and the moving segment but also from the foot support on the ground.
Note: Even though the stabilization is secured also by the muscles located close to the surface we speak about “deep stabilizing system”. However, cannot understand the principle from periphery to the center as preference of the surface muscles. Using inappropriate training some could cause imbalances between the surface and the inside. You can see this every day in the gym, vast majority of people exercise only “visible” muscles. These muscles include the surface abdominal muscles – the famous six pack, the spine erectors but also surface muscles of back, chest and trapezius, muscles of arms etc.
The most frequent mistakes in the gym can cause muscle misbalances, which can be reversed by correct exercising, however it has been experienced that such a retraining takes longer time than practice on newbies.
Principle seven
The trainer as a guide
The trainee is hiring personal trainer or therapist as his guide, who is providing variations, describes ways which are according to his/her opinion practicable. The trainer as the therapist have to always ask for feelings of the trainee who is he working with. This guide should always adjust the ways used to avoid any injuries. He/she should react on things not spoken as well.
The trainee is providing the information by setting of his/her body and this way is communicating this entire message to his/her personal trainer who should listen. If the trainee wants advise, he/she cannot only fiercely ask for certain number of repetitions and speak about fashion or weather. He/she has to be alert, especially if there are disorders of the motion system. The trainer is becoming interpreter of this message, which the body is delivering and which is not recognized by the owner. We cannot trick our body, it always speaks true even though sometimes we do not understand it or, will get the message later in our lives.
We should not only listen to our body, but also listen when it says what to do.
Sometimes the trainer must dig the information needed from his trainee in order to get to the successful result. Using this cooperation, the sensitivity for receiving signals from body is getting much stronger.
The typical example is frequent ignorance of the shoulder blade location. The trainer should help the trainee locate the shoulder blade in different situations of the shoulder joint (push-up, support of the hand, picking up the weight, etc.) That is why he should repeatedly ask the same question: where is the shoulder blade, up or down, does it stick or not to the rib cage and where is it with the inner, lower or upper edge of it? The setting of the shoulder location is entering the subconscious mind with the help of the guide, who is giving the orders for the shoulder blade settings, brain is processing the information and sending the same information to the muscles. The goal is fixation of the shoulder blade, improve the position of chest and this way help with adjustment of shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint), between the socket on the shoulder blade and the hummerus ball.
By using our will (conscious mind) we are not giving the orders to particular muscles, but to the brain. The information is collected and processed in brain, for example from the sensitive brain, which is supplied by information from the periphery. The emotional brain is involved as well as other parts of CNS including programs saved for example in the basal ganglia. Brain calculates information, compares it with the programs and our goal and will decide, how to control muscles.
Brain control motor units around the joint no matter their anatomic nomenclature, to reach the stabile unity. Training, exercising in another name, motor learning is influenced partly by our will and partly involuntarily, so it reacts to signals from periphery (joints, muscles, skin, ears, eyes, etc. )
At the beginning of motor learning, training, the trainer is trying to maximize number of feed-backs for the brain to be saturated from the periphery: he is using various modulations of voice, mirrors, various pushes and other operation on the exercising body parts (pit-patting, rubbing, pushing with finger, sometimes cleavage). In short he will use anything what will improve exercising.
Gradually the trainer is taking these stimuli away until the trainee will learn how to work out by himself.
Principle Eight
Suppressing, activating, helping and guarding.
During exercising therapist, trainer and trainee:
Suppresses the incorrect (inhibits)
To shift away excessive tension, we use manual methodic: therapist is using soft and other techniques, trainer is using post isometric relaxation and its application during stretching, manual help during joint alignment. The drill of breathing influence is essential. The most important suppressing effect is done by brain. That is why we should support its physiological ways of work, triggering of the central-stabilizing programs which is automatically connected with suppressing of the non-physiological excessive tensions during exercising.
Activates correct (facilitates)
During the exercising and establishing of the centralized locations it is essential first help and second induce resistance against the centralization stabilization to activate (enforce) and tighten the central- stabilization program.
The trainer first manually, verbally, etc. helps align the joints and segments (for example shoulder blade to the fixed location) and this way he evokes the reference level for brain. When the trainee is able to evoke this location by him/herself in the simplest conditions, the trainer will try the second, more complicated way, tries to aggravate the conditions for example deviate the segment from the correct position. Both ways are suitable didactical processes which help improve the stabilization programs. In other word “help and defend”.
It was already mentioned, that such a cooperation between the trainer and trainee is not always easy and it is completely far away from the trainer as we can see it often in the gym / so called counter or entertainer. This does not mean that the trainer is not using emotional brain. If so than only for the purpose to contribute the change of the pathological program into physiological. Reasonable trainer is using mostly positive, but if this will help to improve the exercising, also negative emotional timber: is choosing different strength of voice and in the moment of reaching of the correct position he can shout for the trainee to remember this particular positioning. The trainer is using everything what is supporting the progress “from pathology towards physiology at least millimeter by millimeter”. Sometimes it is necessary even distract the attention from the muscles, because flexing hyperactive muscles may distract the exercising. The demand factor of communication lies in its guidance by the trainer (not to be distracted by talkative trainee from the exercising).
Trainer/therapist has to choose all accessible ways. He should try to balance his suverenity (he cannot behave uncertain) and certain humbleness and goodwill to the trainee. He should gradually hand over initiative to the trainee. We could call this submission of gradual fulfilling of the main goal: to get to the subconscious central (functional physiological) joint configuration.
Principel nine
Consider the trainee´s mental state
The drill of joint alignment is described from the point of its configuration, position, alignment, etc. that means from the external point of view. We should be also interested in what is going on in the psyche of the trainee, this we describe as internal point of view.
Individual “external” requirements (head up the crown, shoulders from ears, secure hand support and foot, etc.) are fulfilled better with the help of non-muscle images, sometimes ever funny once (imagine a pot on your head which is pushed up by your crown,  your shoulders are made of wax or honey and are pouring from the ears down, legs are grew into the ground like roots of the tree) and are confront with local and also overall feelings.
your shoulders are made of wax or honey and are pouring from the ears down, legs are grew into the ground like roots of the tree) and are confront with local and also overall feelings.
The trainer can also make the trainee focus using questions and help set the segments this way (Do you feel your shoulder blade how it is ticking to the rib cage now?) Focusing on one body part (for example on the shoulder blade) we can suppress the hyperactivity in other part of the body during the training. (for example in the lower back) and support the practice.
The exercises are often only fragments or imitations of our natural motor movements and we cannot let the subconscious mind control them, for example walking. Using our will, we should have them more or less under control, in order for them to fulfill our goals. Using some kind of inner language without words we communicate for example with our shoulder and shoulder blade and observe what is actually happening with these body parts.
During strength training the “artificial” component of the motion is included here even more than for example during swimming and that is why we have to carefully distinguish, what directs to health and what against it. Everybody has different sense of communication between conscious and unconscious motor motion and we should always take this into account.
The feedback of our actions can be the fact of feeling that the joint works well and painless. Even this feeling is chastening and improving by training. With the health exercising the long term changes are connected. For example, easing of back pain, headaches, hips, etc.
Principle ten
Regulation of stress and rest
The energetic and building blocks deficit caused by training is not only filled in during resting, the growth of run-down nutritional block above the former level is caused, this is called super compensation. In the gym you can get into touch with the most favorable expected super compensation witch is super compensation of protein. For example, runners goal of the specific training and diet is super compensation of glycogen. Super compensation is part of any type of training and influences enzymes and other supporting substances immune particles included. This way exercising might be supporting activity for health. That basically means that by systematic reasonable stress an individual is becoming more resistant to stress.
Loading in in terms of controlled stress with health goals has its own rules. It is important to plan not only the load but also the rest. Especially with regards to sensitive individuals, it is recommended to start with small doses, for example to try 4 exercises per 2-3 sets and wait 2-3 days before next training. It is experienced that the trainees cannot fulfill the central-stabilization goals, because they are getting sick after the work out. If this is happening several times, the mistake is in the planning of training and rest. We have to consider difference between training at home, which is rather energy-saving than training in the gym with weights. That is why after demanding workout a sensitive individual has to rest, fill in nutrients and water. Everybody should consider fact that after training the body is weaker and hence more easily can be attack by viruses and bacteria.
It is experienced that the trainees cannot fulfill the central-stabilization goals, because they are getting sick after the work out. If this is happening several times, the mistake is in the planning of training and rest. We have to consider difference between training at home, which is rather energy-saving than training in the gym with weights. That is why after demanding workout a sensitive individual has to rest, fill in nutrients and water. Everybody should consider fact that after training the body is weaker and hence more easily can be attack by viruses and bacteria.